

Fecal Sludge Management
Comprehensive guidance for implementing safe and sustainable Fecal sludge management across urban and rural India.

Understanding Fecal Sludge Management
What is Fecal Sludge
Fecal sludge is the semi-solid waste that accumulates in on-site sanitation systems such as septic tanks, pit latrines, and holding tanks.
- Composition: Human excreta, water, organic matter, and disease-causing pathogens
- Concentration: More concentrated than sewage, which is highly diluted with water
- Risk: Poses higher risk to public health and environment if not handled safely
What is Fecal Sludge Management
Fecal Sludge Management, or FSM, refers to the safe and hygienic management of fecal sludge generated from on-site sanitation systems.
- Scope: Not limited to treatment alone—includes containment, emptying, transportation, treatment, and safe reuse or disposal
- Objective: Ensure fecal sludge does not contaminate soil, water sources, or living environments
The Challenge
India faces significant challenges in managing fecal sludge across both urban and rural areas due to inadequate collection systems, limited treatment infrastructure, and insufficient institutional capacity. With a majority of households relying on onsite sanitation systems such as septic tanks and pits, unsafe desludging and improper disposal frequently lead to contamination of water bodies, unhygienic surroundings, and severe public health risks.

Fecal Sludge Management (FSM) Value Chain
FSM is best understood through a value chain approach. The FSM value chain consists of four interconnected stages: Toilet Containment System, Emptying & Transportation, Treatment, and safe reuse or disposal. Each stage in this chain is equally important. If any one stage is not managed properly, fecal sludge can leak into the environment, creating health and sanitation risks.
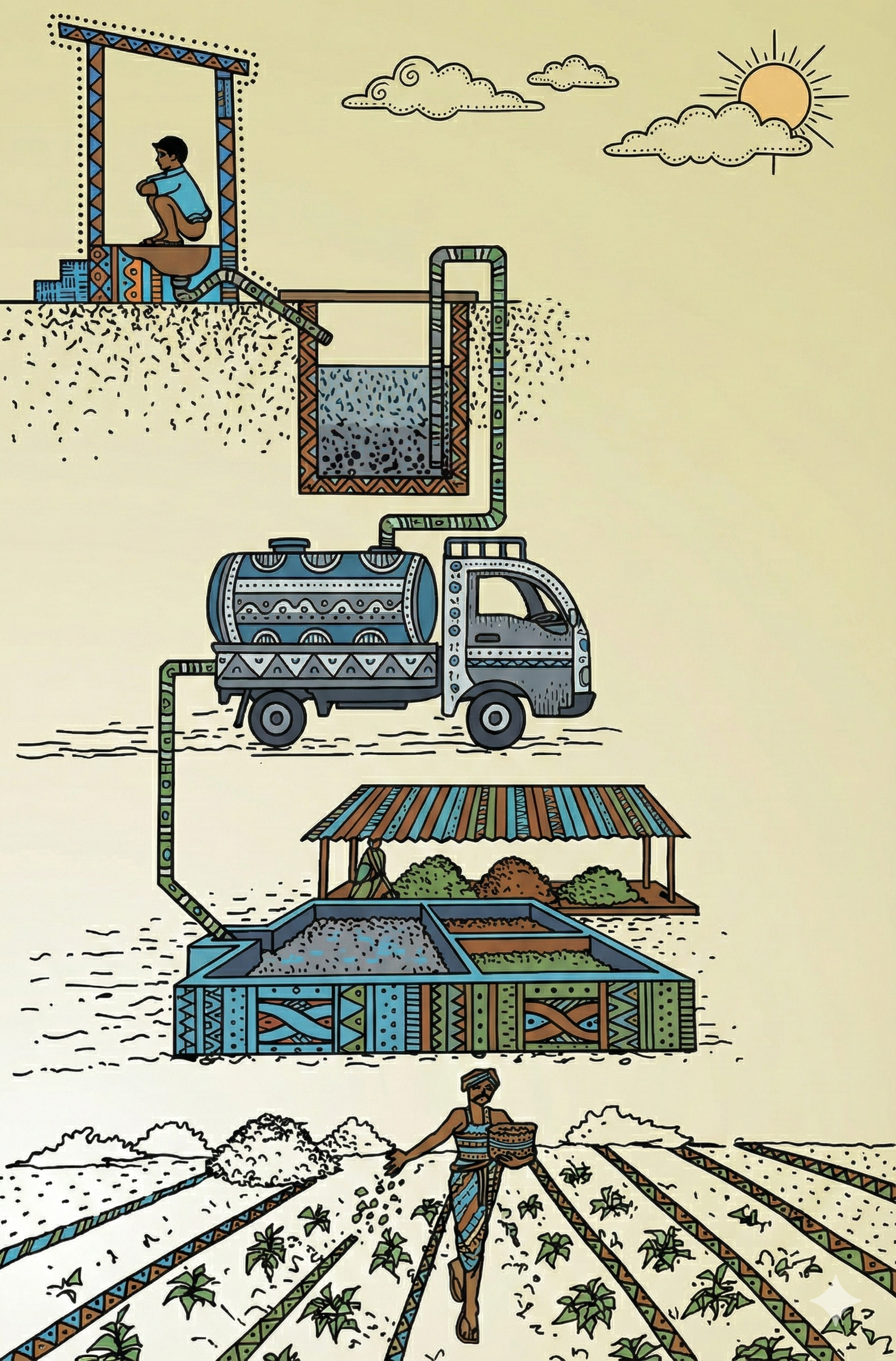
Containment
Identifying toilet containment systems
Conveyance
Emptying and safe transportation
Treatment
Processing sludge for safe reuse
Reuse
Resource recovery from treated products
The Strategy
National Missions
To overcome these challenges, national sanitation missions—including Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban and Grameen) and AMRUT—emphasize achieving safely managed sanitation through systematic Fecal Sludge and Septage Management (FSSM). The missions promote regular desludging, co-treatment at existing STPs/FSTPs, and the adoption of decentralized, cost-effective treatment solutions suited to both small towns and rural settlements.
WASH Institute and FSM
WASH Institute, in partnership with the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA), the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS), state governments, and urban local bodies (ULBs)/Gram Panchayats, has been supporting the development and implementation of scalable FSM approaches. These efforts include technology design, operator training, desludging protocols, treatment plant planning, and monitoring mechanisms.
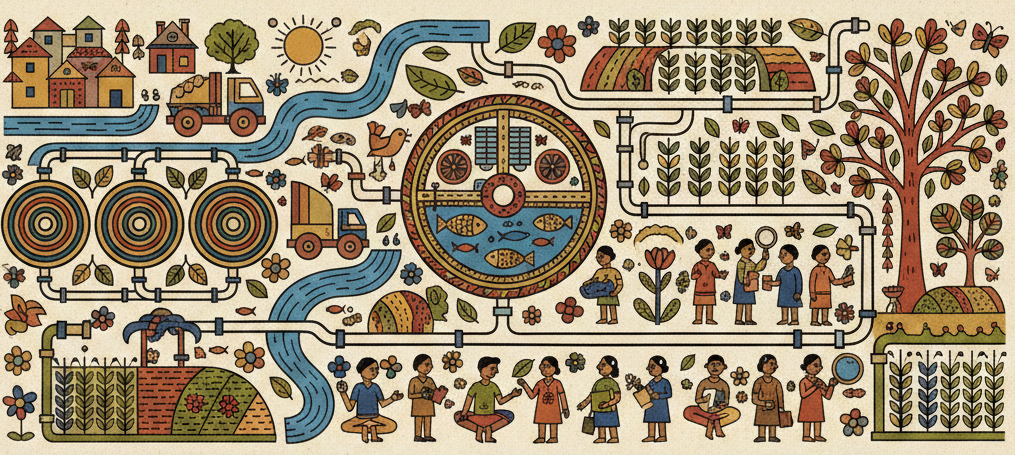

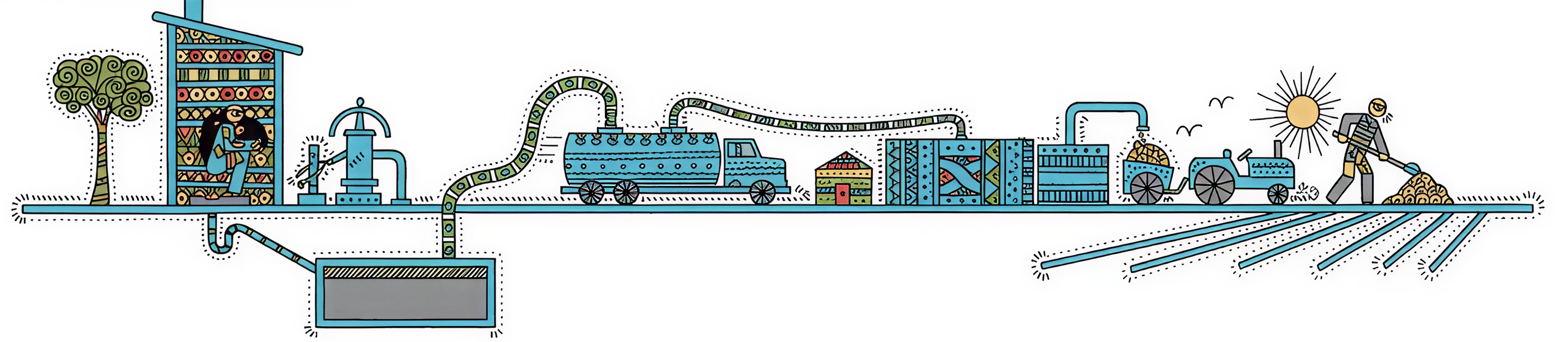
The 5-Stage Framework
Fecal Sludge Management follows a systematic approach through five interconnected stages, from initial containment to final reuse of treated materials.
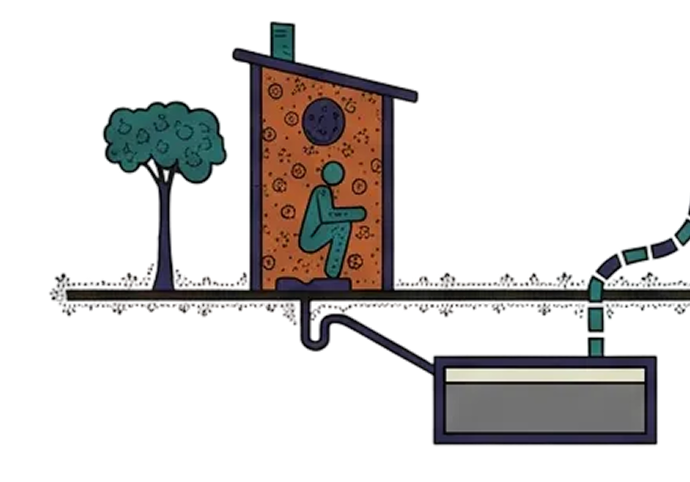

Containment
Identifying containment systems and toilet typologies
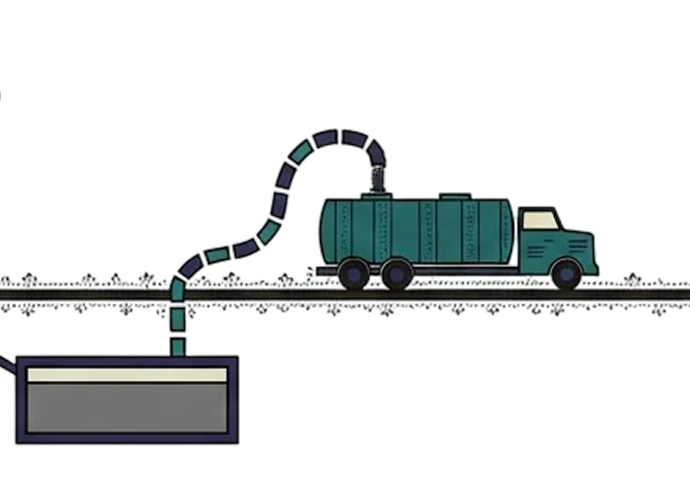
Conveyance
Emptying and transportation to treatment facilities

Treatment
Retrofitting, co-treatment, and FSTP establishment

Reuse
Biosolids and treated water applications

Implementation
Approvals, tendering, monitoring, and commissioning