Common Containment Typologies in India
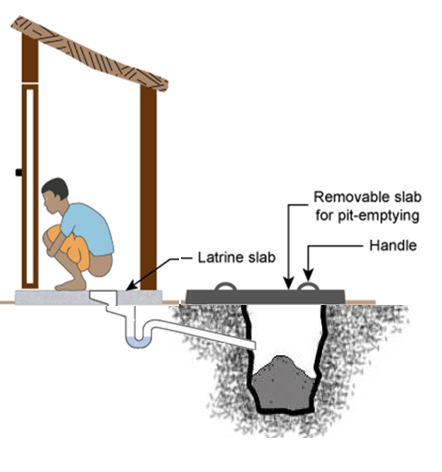
Unlined Single Pit Toilets
- Unlined pit has no structure ("chinai"), and is just an earthen pit ("kaccha gaddha")
- Unlined single pits require manual emptying as they can collapse when mechanized emptying is used
- Any existing unlined pits should be retrofitted or abandoned
- HHs typically abandon unlined pits and dig a new one
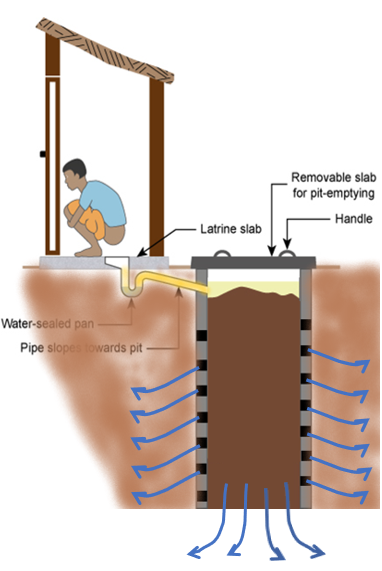
Lined Single Pit Toilets
- Lined pit has a structure ("chinai"), with honeycomb structure or other way of leaving gaps in the wall
- The bottom of lined pit is earthen ("kachha")
- Lined single pits back flow or overflow when full. Households know when to empty them
- Desludging required when pit fills
- To avoid hardening of solids at the bottom it is better to desludge in 5-6 years
- Sludge accumulated per capita per year: 70-80 litres
- Pit filling rate for a family of 5-6 people: 2 years
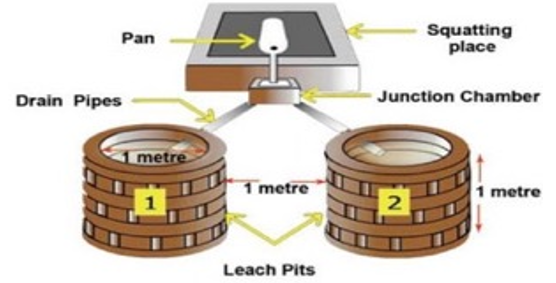
Twin Pit Toilets
- Twin pits have two single pits - when one pit fills the second pit is used
- The full pit is allowed to "rest" for one year or more to dry out
- The contents can be safely emptied manually using a shovel
- Boots, gloves and protective clothing is recommended during emptying
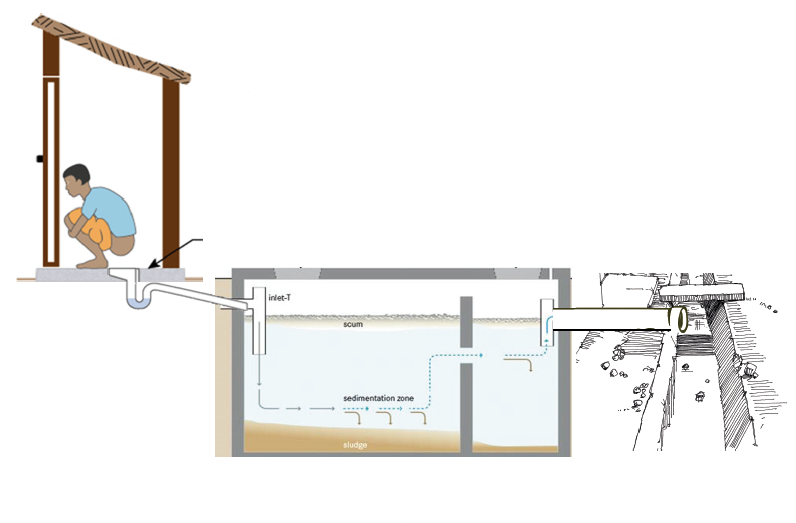
Septic Tank Toilets without Soak Pits
- Septic tank will have watertight walls and floor, therefore water cannot go into earth
- The septic tanks will have outlet pipe from which water overflows when toilet is flushed
- These Septic tanks do not have a soak pit therefore overflow goes into open drains
- This should be avoided by building a soak pit with the septic tank
- Periodic desludging is required ideally in every 3 years
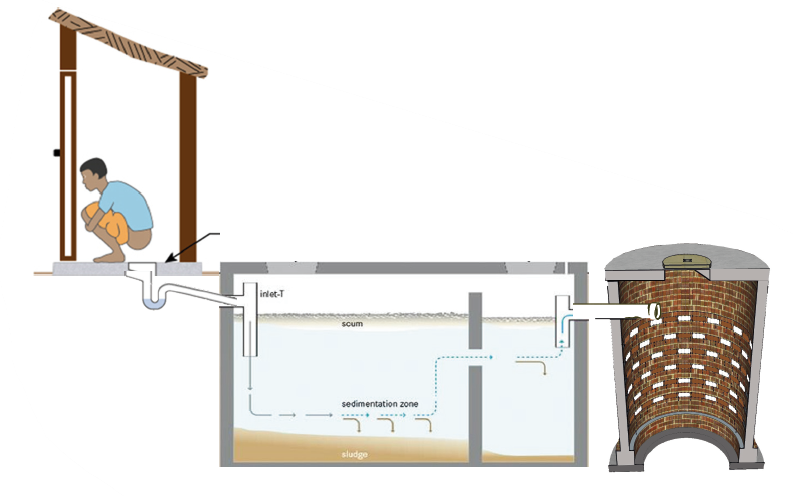
Septic Tank Toilets with Soak Pits
- Septic tank will have watertight walls and floor, therefore water cannot go into earth
- The Septic tank will have outlet pipe from which water overflows when toilet is flushed
- This overflow from septic tank will go into a soak pit ("sokta gaddha")
- Septic tanks with soak pits require periodic desludging to ensure long life of soak pits
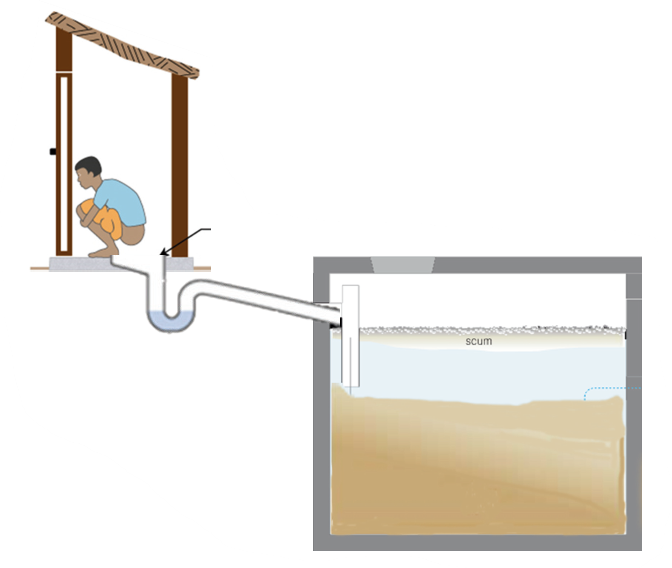
Holding Tanks
- Holding tank will have NO outlet pipe so tank fills frequently
- Wastewater back flows or overflows when the holding tank is full. Households know when to empty them
- Holding tanks fill very quickly as unlike leach pits or septic tanks they neither allow water to seep away or overflow
- Holding tanks have to be emptied frequently
- The contents of a holding tank are more like wastewater and are not considered fecal sludge as they are not "old enough"
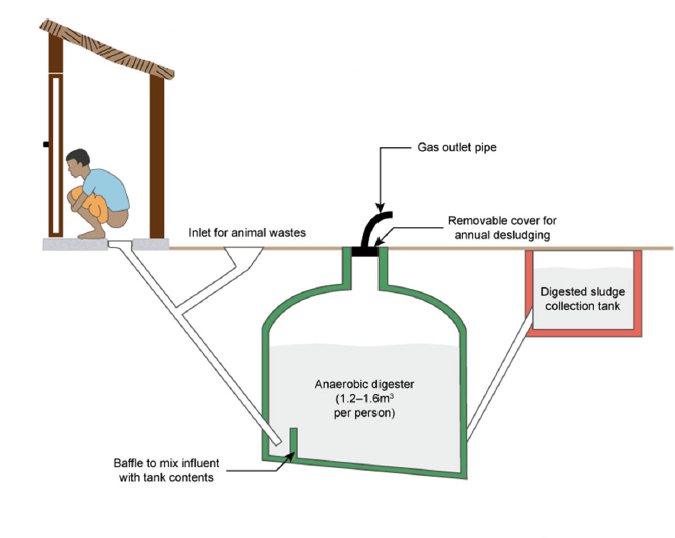
Others
- The toilet is distinctly different from others typologies explained above
- Example: biogas linked toilets, linked to sewer systems
- May or may not require periodic emptying